The European Environment Agency (EEA) and the Eionet network
The European Environment Agency (EEA) is a European Union (EU) agency that provides independent information on the environment. Its primary role is to help the EU and its member and cooperating countries make informed decisions to improve the environment, integrate environmental considerations into economic policies, and support a sustainable transition.
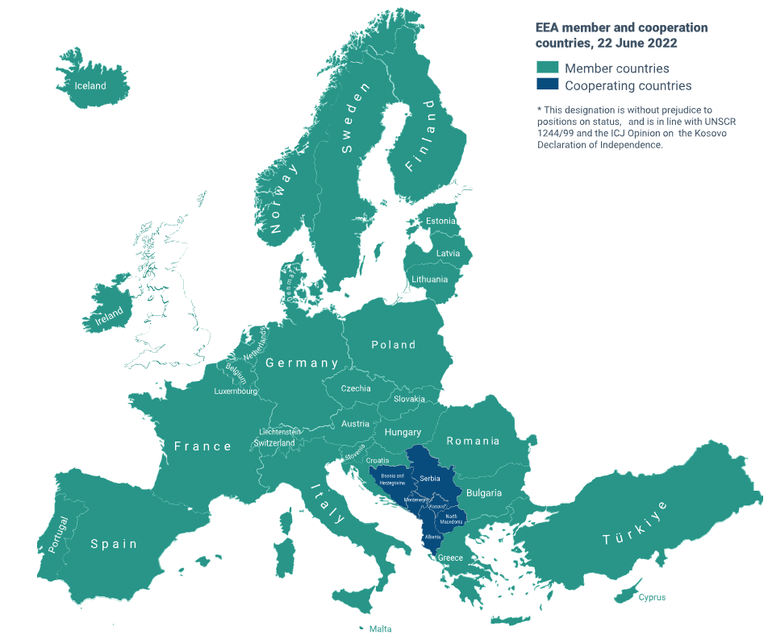
The EEA includes 32 Member Countries (the 27 EU Member States, Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, Switzerland, and Türkiye) and six cooperating countries from the Western Balkans (Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, and Serbia).
Through the Eionet network, the EEA gathers environmental data from European countries and transforms it into shared knowledge, disseminating information and assessments through reports, briefings, articles, press releases, and a range of online products and services, all available on the EEA website.
Fig.1 Member countries
The European Environment Information and Observation Network, known as Eionet, is a partnership network between the European Environment Agency (EEA) and its member and cooperating countries. It involves approximately 3,000 experts and 600 national institutions dealing with environmental issues.
The Eionet network facilitates the collection and dissemination of environmental data and information across Europe. It provides valuable insights for policy makers, non-governmental organisations, scientific and academic communities, businesses, consultancies and think tanks involved in the development, adoption, implementation and evaluation of environmental, climate and sustainable development policies. It also helps citizens to better understand environmental issues and take informed action.
Eionet is composed of National Focal Points (NFPs), European Thematic Centers (ETCs), Eionet Groups, Eionet Thematic Groups, Eionet Working Groups, and Reporters. It includes the 32 EEA member countries and the six cooperating countries.
Cooperation between Eionet members is essential. Network members benefit from each other by sharing knowledge, expertise and experience in areas such as data collection and management, indicator development and environmental assessment. Eionet fosters strong cooperation at different levels (national, regional, European, and international). Communication between Eionet members enhances the quality of data and information at both national and European level. Through benchmarking of environmental performance, countries can learn from each other and strengthen their capacities within existing monitoring and reporting systems.
More information on the Eionet network
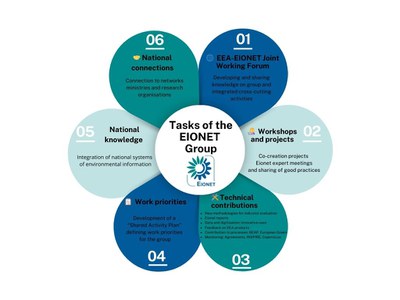
Fig.2 The tasks of the Eionet Network