Climate change
"Climate is what you expect, weather is what you get" (Edward Lorenz, 1961)
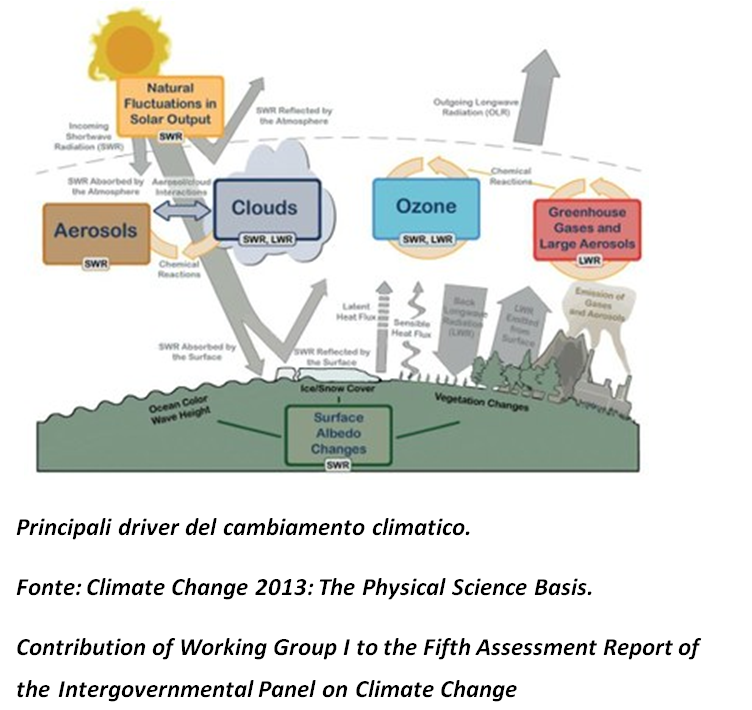 Since the middle of last century fast climate change have been observed by scientists. The earth's climate is subject to seasonal fluctuations, decadal and centuries-old that are related with natural causes such as the Earth's orbit, solar radiation, ocean circulation and volcanic eruptions (climate variability).
Since the middle of last century fast climate change have been observed by scientists. The earth's climate is subject to seasonal fluctuations, decadal and centuries-old that are related with natural causes such as the Earth's orbit, solar radiation, ocean circulation and volcanic eruptions (climate variability).
During the last years, however, more deep and rapid changes of the climate system have been determined by human being, above all due to the increase of greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere. With the first global conference on climate change in 1979, scientists have started to study about how to predict and prevent potential man-made changes in nature and that could have a negative effect on the welfare of humanity.
Sixth IPCC Report
The IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) is the world's highest meeting of climate experts. The IPCC has the task of evaluating the information available in the scientific, technical and socio-economic fields related to climate change, its possible impacts and adaptation and mitigation options. The first volume of the latest IPCC report of 2021 (AR6) confirms that the Earth's climate is warming (the average temperature on the Earth's surface for the period 2001-2020 higher by about 1°C compared to 1850-1900) and that the human impact on the climate system is unequivocal. Climate change involves not only global warming but also an intensification of the hydrogeological cycle. Globally this leads to an increase in evaporation and precipitation. At the regional level, the impacts depend on the region. The Mediterranean basin is considered a particularly vulnerable area (hot spot) to climate change. For the future, a further increase in greenhouse gas emissions could be associated with other significant changes compared to the past, such as further warming, changes in the amount and type of precipitation, rise in sea levels and changes in the frequency and intensity of extreme climatic events (floods, droughts, cyclones, etc.). Even if the growth of greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere were halted during this century, climate change and sea level rise caused by past, current and future human activities would continue for centuries.
-
Rome, ISPRA headquarterMar 24, 2026 09:00 AM — Mar 24, 2026 01:30 PMHydrological Balance and Water Resource Availability: 2025 Update, Seasonal Forecasts and Climate Projections
-
Mar 21, 2026 — Mar 21, 2026International Day of Forests 2026
-
WebinarFeb 19, 2026 09:00 AM — Feb 19, 2026 01:00 PM1st Training of the Italian initiative “C3S NCP for Italy” in support of hydro-climatic and environmental monitoring and climate change adaptation actions
-
Dec 19, 2025A Special Christmas Gift for the Students of the ISPRA V.I.A. Summer School 2024 in Palermo
-
Dec 18, 2025Glacial and Periglacial Hazard in Alpine Environments: A Methodological Framework
- The State of the Environment in Italy 2025: Indicators and Analysis
- Efficiency and decarbonization indicators in Italy and in the biggest European Countries – Edition 2025
- Proceedings of the Conference Days on research and application of ecotoxicological methods. 11th edition " Research and application of ecotoxicological methods: impossible to do without” 26-28 November 2024, Livorno, Chamber of Commerce
- Towards a Monitoring & Evaluation framework for international environmental cooperation: the Italian Ministry of Environment and Energy Security as a case-study
- Atlas 2025. Territories in Transformation
- Environment in Italy: An Overview, 2024 Environmental Data Yearbook
- Greenhouse gas emissions in Italy: reduction targets and emission scenarios
- CO 2 emissions in the national and regional power sector
- Italian Greenhouse Gas Inventory 1990-2023. National Inventory Document 2025
- Italian Emission Inventory 1990-2023. Informative Inventory Report 2025
